Dental Intravenous Sedation (IVS)
The dentist’s use of needles, needle holders (used to inject medical fluids into the gum or the inner cheeks), tweezers/forceps, etc.. generates fear and anxiety in both adults and kids. In fact, the American Dental Association stated that 22% of American adults do not visit dentists out of fear of the dental procedures. For this reason, Dental Intravenous Sedation is quite challenging for dentist, taking into consideration their patients’ fear of needles.
In addition to psychological effects, dental operations (e.g. implants, prosthetic, orthodontic or endodontic treatments, etc.) generate an intense physical pain, which is something both patients and dentists continuously try to avoid.
In order to control anxiety and pain during dental operations, Intravenous Sedation (IVS) or dental anesthesia has become widely used.
IVS consists of the injection of an anti-stress substance into the veins of the patient’s arm or hand back. Anesthesia can be either local or general, depending on the patient’s condition specified by the dentist.
For this procedure, vein finding should be made easier in order to make everything safer and less stressful for the patient, particularly when her/his veins tend to be invisible (Dark skin, drug abuse, babies, old people, etc.).
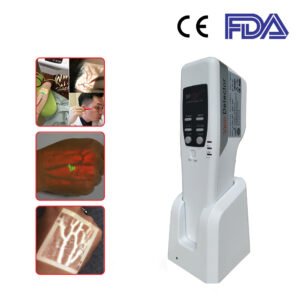
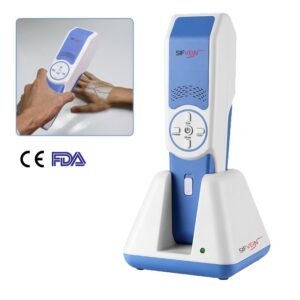
SIFVEIN products are, therefore, crucial in IVS procedures. They are based on the emission of light that illuminates the veins beneath the skin surface, and henceforth, they become more visible.
There are different SIFVEIN devices (handheld/portable, desk type and trolley-supported vein finders) that are adaptable to the different needs of the dentist.
More precisely, the SIFVEIN-4.2 has a blood analysis system with an infrared wavelength of 850 nm and a vein visibility depth of 12 mm maximum.
References:
American Dental Association
Intravenous sedative drugs for dental procedures
How Does IV Sedation Dentistry Work?
Sedation dentistry
[launchpad_feedback]
Disclaimer: SIFSOF is neither responsible for the misuse of the device nor for the device suitability with each clinical application or procedure mentioned in this article.