Pets Ultrasound Scanning
Pets ultrasound scanning is a non-invasive method of imaging, which uses sound waves to help vets visualise a pet’s internal organs and diagnose conditions such as those affecting the heart, liver, kidneys and bladder.
Ultrasound can detect a problem deep within tissue or an organ without invasive surgery. If a sample of tissue is needed, an ultrasound-guided biopsy can be performed after your pet has been given appropriate anesthetics.
Imperative also to note that not just older and sick pets can benefit from ultrasound. Ultrasound can also be used to detect congenital conditions in young pets and certain breeds, even if the pet appears to be perfectly healthy. For older and sick pets, an ultrasound can also be used to make more informed decisions about the course of treatment to take and extend a pet’s quality of life.
The earlier a condition is diagnosed with ultrasound and other diagnostic tests, the sooner a treatment plan can begin. Future ultrasound scans can be compared to track progression of a condition or response to treatment. As with people, early detection can lead to more successful treatment outcomes, and ultrasound is a powerful diagnostic tool to assist veterinarians in helping pets live healthier, happier, longer lives.
Which ultrasound scanner is best for pets scanning?
The color Doppler linear and micro convex SIFULTRAS-5.45.
A microconvex probe is useful in the scanning of small animals. This is for two main reasons, first the animal’s abdomen is small which makes a wide probe less practical. Second the ultrasound waves do not need to travel far very into the body, so a high frequency sound waves would be suitable to produce better quality sound waves.
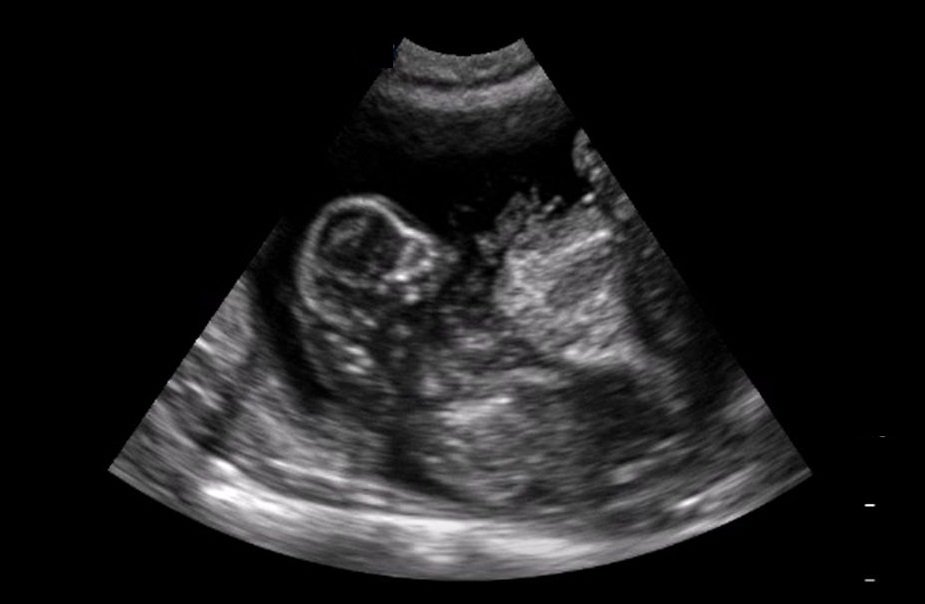
Just like in humans, pets ultrasound scanner can be used to look at the uterus – for example, at the puppies and kittens living there. This allows the practitioner to see at which stage is the pregnancy, and assess how healthy the babies are. Even more importantly, it helps examine the uterus in a sick animal to determine whether or not she has a pyo (a potentially fatal womb infection). Here, by looking for two black circles (sometimes called “shotgun barrels!) which are the two horns of the uterus when they’re filled with fluid.
In addition, it is also used to examine other abdominal organs – the intestines, the kidneys, the bladder, the spleen and the liver. This way, tumours, twists, and other injuries, can be detected without having to open up the patient in surgery. The scanner can also be used to see if there is free blood or fluid inside the abdomen that might indicate internal bleeding; or guide a biopsy needle to a suspicious lump, without needing surgery.
As well as examining tendons and ligaments. This is occasionally useful in dogs and cats (for example, in Achilles tendon injuries), but is usually more an equine vet thing!
Further, Cardiac ultrasonography is usually referred to as echocardiography. Doppler ultrasound is a specialized form of cardiac ultrasound in which the direction and speed of blood flow in the heart and blood vessels can be measured. Color-flow Doppler technology makes it even easier to observe the flow of blood through the heart and important blood vessels.
Ultrasonography allows a look at the beating heart of a dog or cat. In order to measure the amount of blood backing up in the atria (a marker of heart failure), see how thickened or thinned the walls of the heart are, measure the speed of blood passing through a narrowed vessel, or see blood leaking through a damaged valve. This has genuinely revolutionized cardiology for dogs and cats, and with more and better scanners always coming onto the market, it’s going to be more and more important.Ultrasound can diagnose a wide range of medical conditions.
Ultrasound is used to diagnose a wide range of benign and malignant diseases and medical conditions, including:
- stones within the urinary bladder, kidneys or gall bladder
- abnormalities of the gall bladder, urinary bladder, prostate or kidneys
- enlarged lymph nodes
- abnormal blood vessels
- fluid within the abdomen
- disease of the pancreas or liver
- adrenal abnormalities
- uterine infections
- the diagnosis of pregnancy and fetal viability
- diseases of the heart muscle (hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathy) and heart base tumors
- fluid around the heart (pericardial effusion)
- and much more
Since, fur traps bubbles of air and even if the area is wet it won’t give a good insight, so shaving a small patch to scan through is the quite often used solution to this problem.
Results may be seen immediately on a monitor and captured digitally for further evaluation by a radiologist.
[launchpad_feedback]
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SIFSOF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.

