Hydrosalpinx Ultrasound
Hydrosalpinx is a descriptive term and refers to fluid-filled dilatation of the fallopian tube. If the fluid id infected, i.e. pus, then it a pyosalpinx, if bloody, then hematosalpinx.
Infertility due to fallopian tube factors occupies the first place among female infertility. In recent years, there has been an increase in tubal infertility, which may be due to sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea, chlamydia trachomatis infection, mycoplasma infection, intrauterine operations such as multiple abortions.
There are no obvious symptoms after fallopian tube infection, and most of the pelvic examinations are normal. With the gradual promotion and application of ultrasound diagnostic technology and the improvement of diagnostic level, the fallopian tube fluid examination under ultrasound has become the current diagnosis of tubal obstruction One of the convenient methods.
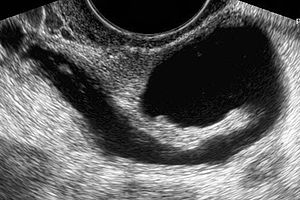
Using standard transabdominal or transvaginal ultrasonography, the appearance of a hydrosalpinx is that of a hypoechoic cystic adnexal mass.
Longitudinal folds that are present in a normal fallopian tube may become thickened in the presence of a hydrosalpinx. The folds may produce a characteristic “cogwheel” appearance when imaged in cross section. These folds are pathognomonic of a hydrosalpinx. Indentations on the opposite sides of the wall is referred to as the waist sign which is a strong predictor of hydrosalpinx. The waist sign in combination with a tubular-shaped cystic mass has been found to be pathognomonic of a hydrosalpinx. Incomplete septa may also give a “beads on a string” sign.
Waist sign and beads on a string are classic features of a hydrosalpinx on ultrasound.
Which ultrasound scanner is best for Hydrosalpinx scanning?
The SIFULTRAS-5.43 uses sound waves to image the tubes, and is somewhat safer than HSG and more comfortable. The best view, most of the time, is obtained with a vaginal ultrasound probe. A normal fallopian tube is usually not visible; a hydrosalpinx appears as a characteristic sausage-shaped fluid collection between the ovary and fallopian tube. The wall of the hydrosalpinx is often thick and flat. Ultrasound provides a quick and painless screen of the pelvic organs and is an excellent first assessment of the tubes
Sometimes the dilated fallopian tube may not show longitudinal folds. If the elongated nature of these folds is not noted, they may be mistaken for mural nodules of an ovarian cystic mass. A significantly scarred hydrosalpinx may present as a multilocular cystic mass with multiple septa (often incomplete) creating multiple compartments. These septa are generally incomplete, and the compartments can be connected. However, with more pronounced scarring, differentiation from an ovarian mass may not be possible.
Further, Color Doppler sonography is used to assess blood flow in a given organ and assesses directional flow as well.
[launchpad_feedback]
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SIFSOF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each vein finder device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.



