CVC : Central Venous Catheter
Central venous catheter placement is essential for careful administration of fluids and drugs in cardiac critical care patients.
Using a real-time ultrasound device in CVC is as important as confirming the correct needle, wire, and catheter position in the vein.
The best suited ultrasound scanner for central venous catheter (CVC) is a linear probe with high frequency and depth 20-50mm.
The SIFULTRAS-3.5 or SIFULTRAS-3.51 has a 10-12-14 MHz to offer the suitable depth reach for CVC.
The use of ultrasound (US) in CVC reduces the number of complications and to increase the safety and quality of CVC placement.
Ultrasound-guided catheter placement impacts the incidence of complications, increases success rates on first attempt, and increases accuracy, thus becoming a standard in clinical practice.
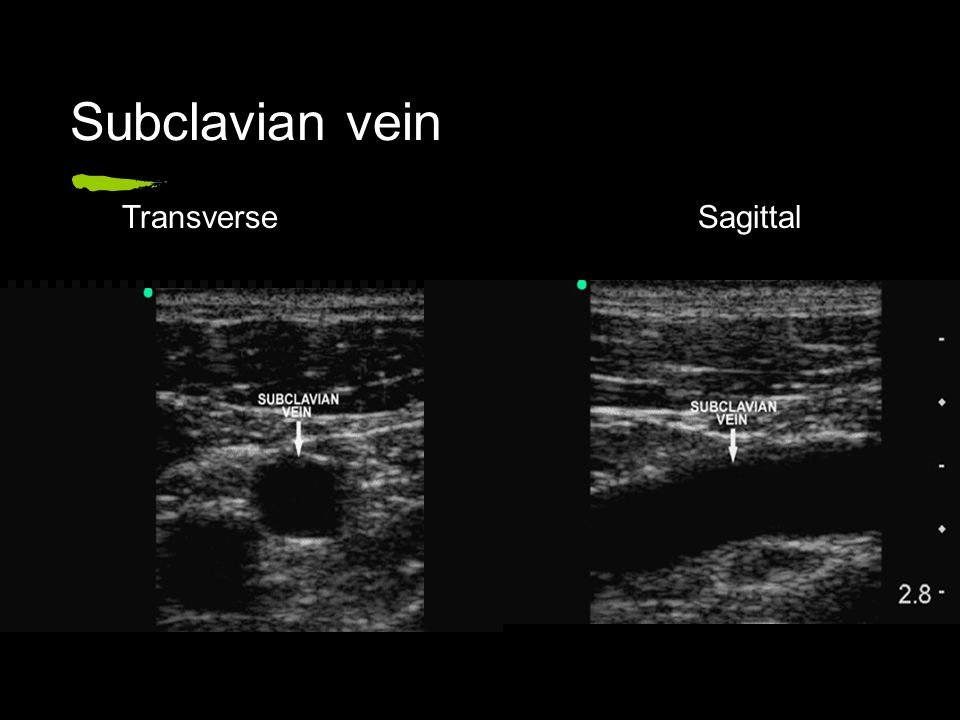
Static and real-time US can be used to visualize the anatomy and patency of the target vein in a short-axis and a long-axis view.
Moreover, the Wireless ultrasound scanner allows the physician to assess the target vein (anatomy and vessel localization, vessel patency).
The appropriate ultrasound machine for CVC in identifying and localizing vessels for catheterization are B mode (bidimensional) and Doppler for flow analysis (arterial or venous).
Selecting the appropriate linear high-frequency (5–12 MHz) probe is critical for obtaining high-quality images; high-frequency provides better resolution of the tissues lying close to the skin surface, which is ideal for vessel visualization.
Superior image quality—US-guided access—allow to identify vessel location, optimal puncture site, and anatomic variants. To a large extent, this helps to avoid venous thrombosis, among other complications.
It is undeniable that ultrasound is an accurate and feasible diagnostic modality to detect CVC malposition and iatrogenic pneumothorax.
A specially trained nurse called a Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS) will insert the CVC at your bedside, anesthesiologist might as well.
[launchpad_feedback]
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SIFSOF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.