Soft Tissue Foreign bodies Ultrasound
Penetrating injuries and suspected retained foreign bodies are a common reason for emergency department visits. Sonography is a useful modality in detection and localization of radiolucent foreign bodies in soft tissue which can avoid misdiagnosis during primary emergency evaluation.
Ultrasonography (US) allows detection of a variety of soft-tissue foreign bodies, including wood splinters, glass, metal, and plastic, along with evaluation of their associated soft-tissue complications.
Which ultrasound scanner is used to detect foreign bodies in soft tissue?
A high-frequency (7.5-MHz and higher) SIFULTRAS-5.34 linear-array transducer is optimal for US evaluation of soft-tissue foreign bodies. The device offer improved spatial resolution, achieving anatomic detail of small structures with high accuracy and may identify foreign bodies (FB) under 1mm in diameter.
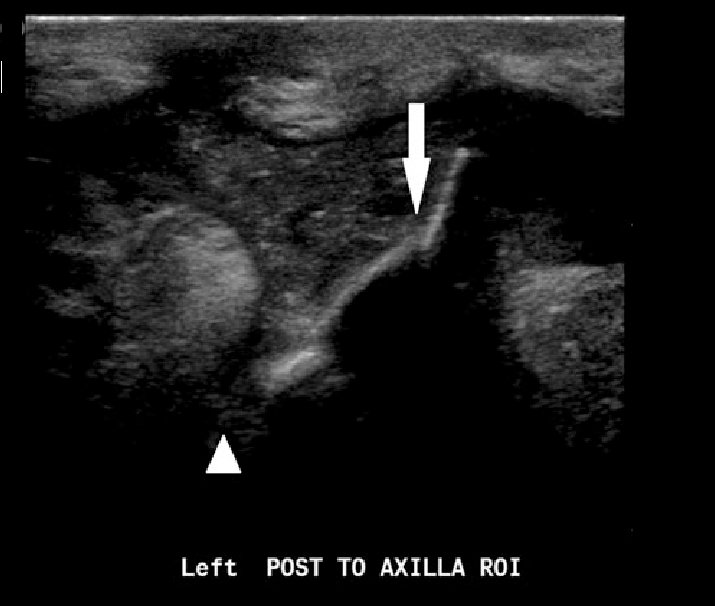
US allowed localization of a foreign body superficial to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon, and removal was easily accomplished in the emergency department.
In another patient, US allowed localization of a foreign body superficial to the flexor digitorum profundus tendon but also demonstrated flexor tenosynovitis, which necessitated surgical incision and drainage. US allowed correct identification of a complete rupture of the posterior tibial tendon secondary to laceration by a glass foreign body.
Further, ultrasound allows examination of the surrounding muscles, tendons, ligaments, and neurovascular structures and assessment of associated injuries. Soft-tissue infection is by far the most common complication of a penetrating foreign body, with nerve injury a distant second.
US allowed identification of foreign bodies in the soft tissues superficial to intact plantar fascia and plantar tendons.
The area of interest is scanned in both the longitudinal and transverse orientations, with attention to detection of a foreign body and its associated posterior acoustic shadowing or reverberation.
US allows determination of the precise location of the foreign body, as well as its size, shape, and orientation, and aids skin marking for removal. The surrounding soft tissues are also examined for fluid collections, tendon disorders, and injury to neurovascular structures.
For proper technique, requires a slow and meticulous examination, especially in cases of small FB less than 1cm in length, where they can be unnoticed, also in anatomical areas like hands and feet, where echogenic structures exists such as sesamoid bones that can result in false positives.
Another aspect to consider is that echogenicity of a FB also varies according to the orientation of the long axis FB with respect to the skin. When the FB is parallel to the skin the visualization is maximum. Moreover it should be noted that small punctate structures may correspond to bulky FB if the cutting plane was carried by the short axis, as for example in the case of thorns.
S is an inexpensive, portable, and readily available imaging modality for superficial soft tissues without the risk of ionizing radiation. US has emerged as the study of choice for detection of radiolucent foreign bodies.
This procedure is usually done by emergency specialists or orthopedists.
References: Soft- tissue foreign bodies: Diagnosis and removal under ultrasound guidance, US of Soft-Tissue Foreign Bodies and Associated Complications with Surgical Correlation.
[launchpad_feedback]
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SIFSOF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each ultrasound scanner device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.



