Carotid Artery Stenosis Ultrasound Diagnosis
Carotid artery stenosis (CAS), atherosclerotic narrowing of the extracranial carotid arteries, is a risk factor for ischemic stroke. Which makes it clinically significant.
The clinical finding of a carotid bruit on auscultation is non-specfic; therefore, hemodynamically significant CAS cannot be determined by physical examination alone
Of the imaging modalities available for diagnosis of CAS, Doppler ultrasound is often used because it requires no radiation or intravenous contrast and is relatively inexpensive compared with computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography.
Consequently, Ultrasound carotid stenosis is the most common diagnostic technique. Changes in blood flow velocity at the point of maximum stenosis, together with haemodynamic changes in proximal regions (common carotid artery) and distal regions (poststenotic internal carotid, ophthalmic artery, and the circle of Willis), allow us to measure carotid stenosis precisely.
In addition, Ultrasound assessment of carotid arterial atherosclerotic disease has become the first choice for carotid artery stenosis screening, permitting the evaluation of both the macroscopic appearance of plaques as well as flow characteristics in the carotid artery.
Which ultrasound scanner is used for Carotid Artery Stenosis diagnosis?
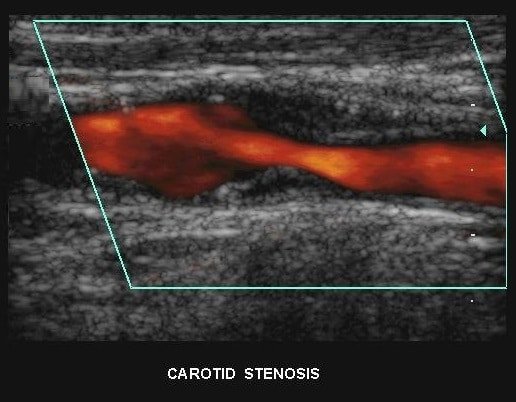
Arterial stenosis should preferably be assessed using color Doppler ultrasound SIFULTRAS-3.3 to capture images of the arterial wall in longitudinal and transverse planes. Longitudinal images may be difficult to capture in some patients, and in such cases it may be useful to obtain a coronal projection of the artery by placing the transducer behind the sternocleidomastoid. Viewing the arterial wall is a means of measuring carotid intima-media thickness and determining if and where atheromatous plaque may be present.
Carotid stenosis is usually diagnosed by ultrasound scan of the neck arteries. This is the first imaging option and usually used for follow up and observation as it involves no radiation and no contrast agents that may cause allergic reactions.
A Doppler ultrasound study a technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel. It is usually part of this exam. It’s most frequently used to screen patients for blockage or narrowing of the carotid arteries.
Vascular imaging techniques used to diagnose carotid stenosis have advanced considerably in recent years, especially ultrasound imaging. Although different expert consensus groups have attempted to set down criteria for diagnosing and quantifying carotid stenosis using ultrasound they do not agree on which haemodynamic parameters should be used.
References: Ultrasound assessment of carotid arterial atherosclerotic disease, Ultrasound measurement of carotid stenosis: Recommendations from the Spanish Society of Neurosonology, Ultrasound – Vascular, Carotid artery stenosis echocardiography or ultrasound.
[launchpad_feedback]
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SIFSOF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or random generalizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each vein finder device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.



