Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis (HPS) is the most frequent surgical condition in infants in the first few months of life. The condition is characterised by thickening of the muscular layer and failure of the pyloric canal to relax resulting in gastric outlet obstruction.
Ultrasound (US) is the preferred diagnostic modality as it is a non-invasive technique, allowing direct observation of the pyloric canal morphology and behaviour. It is important to carry out a systematic and dynamic study and to be aware of the common technical difficulties and how to overcome them.
Which ultrasound scanner is best for Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis imaging?
A high-frequency transducer SIFULTRAS-5.17 adjusted to the size of the patient and the depth of the pylorus should be used. In the majority of the cases a 6–10 MHz linear probe will provide the depth required to visualise the pylorus
The US examination allows the radiologist to perform a brief clinical history, which can reveal essential clues to the diagnosis.
US is the first modality of choice when there is clinical suspicion of HPS, as it is non-invasive and does not use radiation, which is a crucial advantage in children. It is also a commonly available with relatively low cost. US also allows a dynamic study with direct observation of the pyloric canal morphology and behaviour. The US should be performed by an experienced radiologist. Having a systematic approach will improve the sensitivity of the technique.
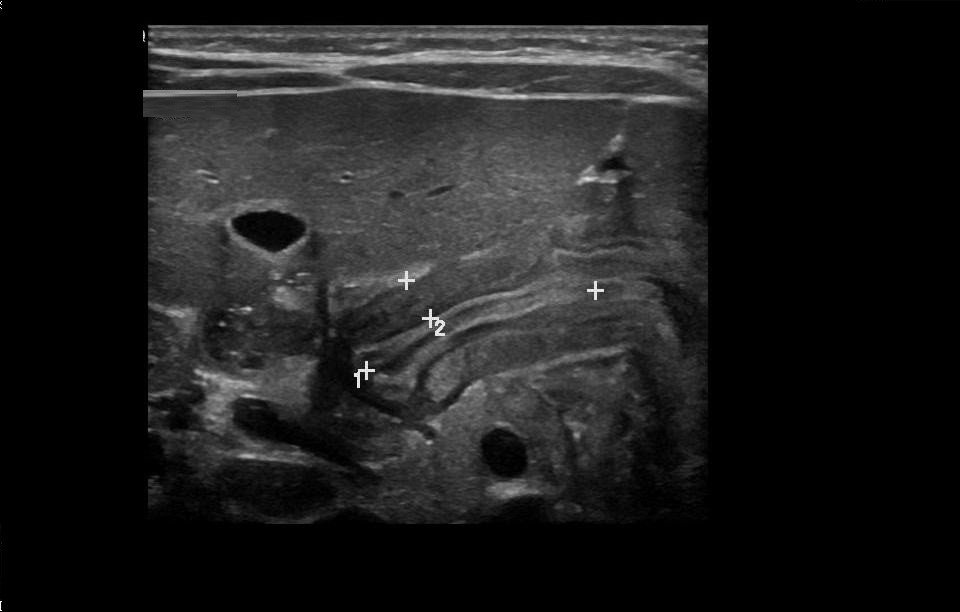
After identifying the gallbladder, the pylorus measurements could be then assessed. This dynamic evaluation is vital, to Visualize the passage of the gastric content through the pylorus, distending the antropyloric region.
Pyloric US examination is a dynamic investigation, which should be performed in a systematic way. The radiologist should be aware of the pitfalls of the examination and how to overcome them. It is important to be familiar with the normal and hypertrophied pyloric appearances, as this will provide a greater diagnostic confidence, assisting in early diagnosis and improving the management of infants with HPS.
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis: tips and tricks for ultrasound diagnosis
[launchpad_feedback]
Disclaimer: Although the information we provide is used by different doctors and medical staff to perform their procedures and clinical applications, the information contained in this article is for consideration only. SIFSOF is not responsible neither for the misuse of the device nor for the wrong or randomgeneralizability of the device in all clinical applications or procedures mentioned in our articles. Users must have the proper training and skills to perform the procedure with each vein finder device.
The products mentioned in this article are only for sale to medical staff (doctors, nurses, certified practitioners, etc.) or to private users assisted by or under the supervision of a medical professional.